Types of Structural Cracks in Concrete Beams | Causes of Cracks in Concrete Beam
In this Article today we will talk about the Types of Structural Cracks in Concrete Beams | Causes of Cracks in Concrete Beam | Concrete beam | Structural Cracks | Fixing Structural Cracks | Concrete Cracks Types | Types of Crack in Concrete | Why Concrete Crack | Shear Cracks in Beam | Flexural Cracks in Beam | Vertical Cracks in Beam | How to Repair Cracks in Concrete Beam
Types of Structural Cracks in Concrete Beams:
Several types of cracks occur in concrete beams due to shear stress called as shear crack, reinforcement corrosion, insufficient rebar cover, bending stress and compression failure.
The occurrence of various crack patterns in the building mostly takes place during construction and/or after completion. A building component develops cracks whenever the stress in the components exceeds its strength. Stress in the building component is caused by externally applied forces/loads.
Almost all the types of cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams are fundamentally defined by the principle cause or mechanism associated with the function of cracks. Causes of Cracks in Concrete Beam
Types of Concrete Cracks in Beams:
Here we have tried to provide you with an overview of almost all the types of cracks occurred in RCC beams. Fixing Structural Cracks
01. Flexure Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
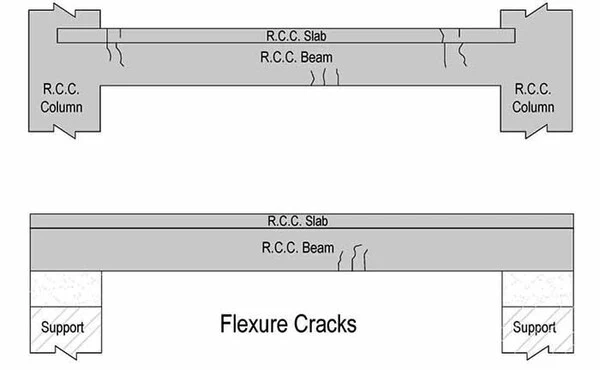
Member
- RC Beam Shear Cracks in Beam
Important Characteristics
- Originates in maximum moment region (in above image this region is in centre of the beam, it varies as per support Conditions of beam)
- May be single or in groups
- Maximum width at bottom/top of beam Vertical Cracks in Beam
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Flexural capacity of the beam is inadequate.
- When Cross section of the beam or main reinforcement in beam is insufficient.
- i.e. it is loaded more than defined loads. Vertical Cracks in Beam
02. Shear Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
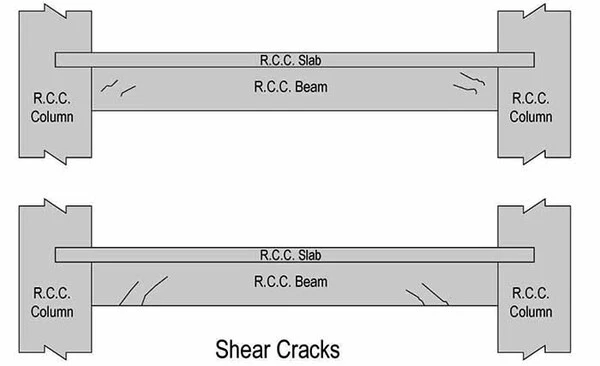
Member
- RC Beam Vertical Cracks in Beam
Important Characteristics
- Originates nearer to supports.
- Maybe single or in groups.
- Maximum width at neutral axis region or at bottom of beam. Flexural Cracks in Beam
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Shear Capacity of the beam is inadequate.
- Cross section or torsional reinforcement insufficient.
- Both here happen due to loading more than designed load.
03. Torsional Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
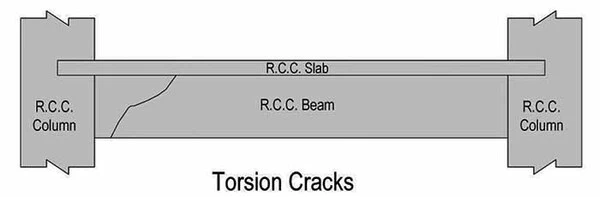
Member
- RC Beam
Important Characteristics
- Originates nearer to maximum torsion region.
- Single generally uniform width. Appears over the whole periphery in helical form
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Torsional strength of the beam is inadequate.
- Cross-section or torsional reinforcement insufficient.
04. Corrosion Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
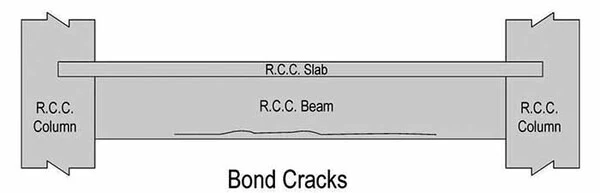
Member
- RC Beam
Important Characteristics
- Runs along the line of reinforcement.
- Uniform width in general
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Bond between reinforcing bars and concrete not satisfactory.
- May be due to corrosion of bars/fire damage.
05. Shrinkage Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
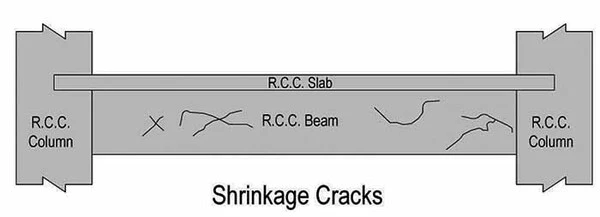
Member
- RC Beam
Important Characteristics
- No regular pattern or thickness and in general superficial.
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Curing is inadequate or no control over water-cement ratio.
- Usage of an excessively rich mix.
- Shrinkage reinforcement, if any, insufficient.
06. Sliding Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
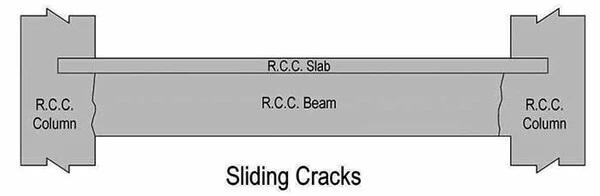
Member
- RC Beam Fixing Structural Cracks
Important Characteristics
- Runs vertically at the edge of supports.
- Maximum width at bottom of the beam.
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Concrete in a beam is disturbed at an early age when adequate strength not realised.
- Maybe due to disturbance of formwork at green stage or early deshuttering.
07. Tension Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Beams
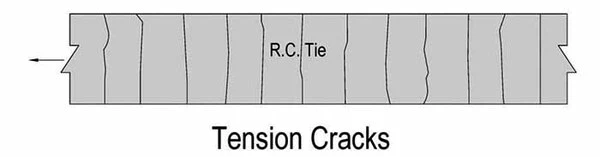
Member
- Reinforced Concrete Tie Flexural Cracks in Beam
Important Characteristics
- Appear over whole periphery. Generally over the whole length of the member.
- Parallel to each other.
- Uniformly observed
Causes or Possible Reasons
- Capacity of the member in tension is inadequate.
- Tensile reinforcement is insufficient.
OTHER POSTS:
-
How to Calculate the Cutting Length of Spiral Bar or Helix Bar | BBS
-
How to Calculate Cutting Length of Bent Up Bar in Slab
-
How to Calculate Unit Weight of Steel Bars | Steel Weight Formula
-
How To Find Out The Cutting Length Of Main Bars & Circular Rings
-
Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) | BBS Step by Step Preparation | Excel Sheet
-
Bar Bending Schedule Basic Formulas | BBS Formula | What is BBS
FAQs:
Conclusion:
Full article on Types of Structural Cracks in Concrete Beams | Causes of Cracks in Concrete Beam | Concrete beam | Structural Cracks | Fixing Structural Cracks | Concrete Cracks Types | Types of Crack in Concrete | Why Concrete Crack | Shear Cracks in Beam | Flexural Cracks in Beam | Vertical Cracks in Beam | How to Repair Cracks in Concrete Beam. Thank you for the full reading of this article in “The Civil Engineering” platform in English. If you find this post helpful, then help others by sharing it on social media. If any formula of BBS is missing from this article please tell me in comments.


7 Comments
good
very good
Thanks for the comments please visit more articles by clicking on “All Posts” tab of the Menu Bar
Very Good information
Thanks for the comments please visit more articles by clicking on “All Posts” tab of the Menu Bar
Very educative Engineer Wassem Raja.
thanks