What Is Honeycomb In Concrete | Cause of Honeycomb In Concrete | Concrete Honeycomb Repair | Causes on Honeycomb.
In this Article today we will talk about the Honeycomb in Concrete | Concrete Honeycomb Repair | Causes of Honeycomb in Concrete | Types of Honeycomb in Concrete | Effects of Honeycomb in Concrete
What Is Honeycombing In Concrete ?
Honeycombs are the hollow spaces and cavities left in concrete mass on surface or inside the concrete mass which is caused by the mortar not filling the spaces between the coarse aggregate particles

Types of Honeycombs:
Small Size Honeycombs:
Depth is less than 25mm
Moderate Size Honeycombs
Deeper than 25mm but steel bars have not exposed. Types of Honeycomb in Concrete
Larger Size Honeycombs
Deeper than 25mm & bars have come out
OTHER POSTS:
-
Method Statement for Formwork, Reinforcement and Concrete Works
-
Method Statement for Concrete Repair Works | Structural Works
-
Things to Check Before Column Concreting | Concrete Pouring in Column
Where can we find Honeycombs ?
Honeycombs which are on sides and bottoms are visible to naked eyes and can be detected when shuttering is removed. Honeycombs which are inside mass of concrete can only be detected by advanced techniques like ultrasonic testing etc.

Effects of Honeycombs:
- Water and air enters inside
- Rusting and corrosion of reinforcement
- Reduce durability
- Less structural strength
- Reduces the load bearing capacity
Causes for Honeycombs:

Poor Workability:
- Slump Test can be used to find out the workability of concrete. If the slump is less workability is less. Types of Honeycomb in Concrete
- Workability might be less because
- Low water content
- Finer cement particles
- High temperature
- Ratio of fine-to-coarse aggregate being low

Improper Compaction:

- The purpose of compacting concrete by vibration is the elimination of entrapped air and forcing the particles in to a closer configuration that will definitely build the more strength.
- Over vibration would make the concrete segregated while under vibrated concrete would have honeycombs in it.
- Poor concrete compaction occurs due to ineffective vibration or rebar congestion.
- Under Vibration, Inserting at angles, touching reinforcement and touching formwork is also cause of honeycomb in concrete.
Improper Cover & Placement of Rebar:

- Rebar congestion – If rebar is placed too close together or too close to formwork it will trap the larger pieces of aggregate while the mortar in the mixture may not pass through & interfere with concrete flow and vibration.
-
Insufficient cover – When number of cover blocks to rebar is less or the size of the cover blocks is not sufficient, honeycombs might occur.

Movement of Formwork & Grout leak:
- When joints of formwork are loose there can be leakage of grout through these joints. Honeycombs occur.
- Increased water content also results in bleeding, hence, increased water content can also mean that cement slurry (grout) will escape through the joints of the formwork.

Poor Grading of Aggregate:
- Presence of more percentage of bigger size of aggregate in concrete also prevents concrete to fill narrow spaces between the reinforcement rods.
- Voids often occur because aggregate is too large to pass through a condensed area of reinforcement.

Practices to minimize Honeycombing in concrete:
- Use a mix with appropriate workability for the situation in which it is to be placed.

- Ensure the mix has sufficient fines to fill the voids between the coarse aggregate.
-
Use proper methods of compacting and ensure concrete is fully compacted.
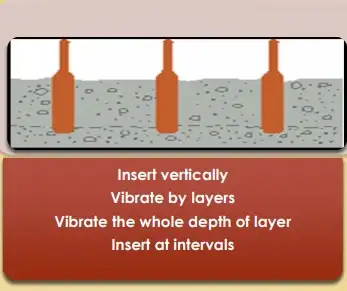
- Use proper methods of placing concrete
- Avoid segregation
- Avoid delays
- Pour by layers

- Proper cover block thickness should be maintained for particular concrete structures.(Eg : walls, columns, staircases – 25mm, slabs- 40mm, beams- 50mm, pile caps- 75mm).
- Sufficient cover blocks should be provided.
- Rebar congestion can be minimized by having larger (that is, lesser) rebar or by increasing the sectional dimensions of elements where possible.
- Ensure the reinforcement layout and the section shape will permit the concrete to flow around the reinforcement and completely fill the forms.
Practices to minimize Honeycombing in concrete:

- Check that the formwork is rigid and well braced, the joints are watertight and any penetrations through the formwork. e.g. form ties are properly sealed.
- Provide enough supports to formwork.
- Defective formworks and accessories should be repaired or replaced to prevent grout leakage during concreting.
Concrete Honeycomb Repair:
For Small & Moderate Honeycombs:

- Hack and remove the loose particles in order to appear sound surface.
- Surface is cleaned by water jet to obtain dust free surface.
- Construction grout is applied.
- Texture and color should then be matched for aesthetic finish.
- Curing is done.
For large Honeycombs:

- Hack & remove the weak concrete to expose sound concrete surface.
- To keep clearance around reinforcement 12mm thick concrete layer is removed.
- By using water jet surface is cleaned.
- Barra emulsion is used as a bonding agent.
- Over the wet surface Barra emulsion is applied and before drying, 1:2 cement mortar is applied.
- After mortar has set sufficiently, final surface is prepared by trowel.
- Texture and color is matched for aesthetic finish.
- Curing is done.
FAQ’s
What is Honeycombing of concrete ?
Honeycombs are hollow spaces and cavities left in concrete mass on the surface or inside the mass where concrete could not reach. Improper vibration and workability of concrete are main causes of honeycombs in concrete.
1. How to Fix Honeycombing in Concrete ?
- Isolate the affected area by removing layers of honeycombing until suitable concrete is exposed. Effects of Honeycomb in Concrete
- Thoroughly clean the area to be repaired and remove all dirt and loose aggregate.
- Wet the cleaned area prior to applying non-shrink grout.
- Texture and colour should then be matched for aesthetic finish.
2. What Is Honeycombing in Concrete ?
Honeycombing refers to voids in concrete caused by the mortar not filling the spaces between the coarse aggregate particles. It usually becomes apparent when the formwork is stripped, revealing a rough and ‘stony’ concrete surface with air voids between the coarse aggregate. Effects of Honeycomb in Concrete
3. What Causes Honeycombing in Concrete ?
Honeycombing is caused either by the compaction not having been adequate to cause the mortar to fill the voids between the coarse aggregate, or by holes and gaps in the formwork allowing some of the mortar to drain out of the concrete.
4. How to Repair Concrete Honeycombing ?
- Remove loose concrete or loosened aggregate by hammer or wire brush. Prevent the application of large forces such as electrical chippers to avoid sound concrete damage around the honeycomb area.
- Clean any dirt or loose material from the area.
- Wet the cleaned area before applying the repair material.
- Fill small voids and cracks using a mechanical injection pressure pump with a suitable material such as non-shrinkage epoxy grout.
- If the honeycomb covers a large area, you may need to create a patch hole to ensure proper bonding. Effects of Honeycomb in Concrete
5. Is Honeycombing in Concrete Bad ?
Small, shallow areas of honeycombing are probably mainly cosmetic. However, deeper areas will lead to a local reduction in the protection to the reinforcement from the concrete cover and hence possibly durability problems in the future.
6. How to Prevent Honeycombing in Concrete ?
Avoid honeycombing by using appropriate concrete mixtures with sufficient workability, proper placement and consolidation techniques. Honeycomb, subsidence cracks, cold joints and excessive surface air voids are common surface blemishes associated with ineffective concrete consolidation.
7. How to Repair Honeycomb in Concrete ?
- Remove loose concrete or loosened aggregate by hammer or wire brush
- Clean any dirt or loose material from the area.
- Wet the cleaned area before applying the repair material.
- Fill small voids and cracks using a mechanical injection pressure pump with a suitable material such as non-shrinkage epoxy grout.
Conclusion:
Full article on Causes of Honeycomb in Concrete | Types of Honeycomb in Concrete | Effects of Honeycomb in Concrete. Thank you for the full reading of this article in “The Civil Engineering” platform in English. If you find this post helpful, then help others by sharing it on social media. If you have any question regarding article please tell me in comments.

