How to Calculate Superelevation in Road | Purpose | Superelevation Formula | Purpose of Providing Superelevation | Methods of Superelevation
In this Article today we will talk about the What is Superelevation | Superelevation of Road Formula | Maximum Superelevation | Methods of Superelevation | How to Calculate Superelevation in Road | Superelevation Calculation | Advantages of Superelevation | Superelevation in Highways
What is SuperElevation | How to Calculate Superelevation in Road
Superelevation on the horizontal curve is one of the most important features in the construction of the roads. It is very essential to provide superelevation in roads for the safe movement of vehicles on the curved portion of the roads.

It helps the fast-moving vehicles to safely pass through the curved portion of the roads with stability. Superelevation Calculation
Superelevation Definition
The inward transverse inclination which is provided to the cross-section of the pavement of road at the horizontally curved portion of the roads is known as superelevation.
Superelevation is also known as Cant or Banking. Superelevation Calculation
Superelevation in roads is basically provided on the horizontally curved portion of the roads in which the outer edge of the road pavement is raised with respect to the inner edge, thus providing a transverse slope throughout the length of the horizontal curve of the road.
This transverse inclination to the surface of the road pavement is known as Superelevation. Superelevation Calculation
Purpose of Providing Superelevation in Roads
- The main aim of providing superelevation is to counteract the effect of centrifugal force acting on the moving vehicle.
- To prevent the damaging effect on the surface of the roads due to improper distribution of load on the roads.
- To help the fast-moving vehicles to pass through a curved path without overturning or skidding.
- To reduce the maintenance cost of the road on the curved portion.
- To ensure the smooth and safe movement of vehicles and passengers on the curved portion of the roads. Superelevation Calculation
Superelevation is expressed as the height of the outer edge of the pavement with respect to the width of the pavement. Superelevation of Road Formula
Derivation of Super Elevation:
As per the figure, the below forces are acting on a car
In order to find out the angle of elevation (Super Elevation) the “tan” formula is used
From above fig, tanθ = Opposite Side⁄Adjacent Side
therefore, tanθ = E⁄B
The below forces are acting on the vehicle as mentioned in figure:
Weight of the vehicle = W kg (↓) ;
Centripetal force = P (→);
Frictional forces = F1 & F2 (← );

You can check out the below figure more idea. Hence, P.Cosθ = W.Sinθ+F1+F2
where, F = fR
P.Cosθ = WSinθ + fR1 + fR2
= W.Sinθ + f(R1 + R2)
= W.Sinθ + f(PSinθ+WCosθ)
P.Cosθ-f.PSinθ = W.Sinθ+f.WCosθ
Divide with “W.Cosθ”; Maximum Superelevation
(P.Cosθ-f.PSinθ)⁄W.Cosθ = (W.Sinθ+f.WCosθ)⁄W.Cosθ
P⁄W -(f.P⁄W)tanθ = tanθ + f
P⁄W (1-f.tanθ) = tanθ+f
P⁄W = (tanθ+f)⁄1-f.tanθ
P⁄W = e + f But,
P⁄W = V2/ gR
Therefore, e + f = V2/ gR
Where, Maximum Superelevation
e = rate of Super elevation in %
V = velocity of vehicle in m/s
f = lateral friction factor = 0.15
g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s2
R = radius of circular curve in meters.
If velocity is in KMPH then e + f = V2/ 127R Maximum Superelevation
Super Elevation Formula

The above formula is used only to calculate one of the missing value either e or f or V or R for design purpose consider the below procedure. Maximum Superelevation
How to Calculate Superelevation in Road:
Design procedure of Superelevation / Banking of road
Design procedure includes following steps Methods of Superelevation
Step – 1: How to Calculate Superelevation in Road
Calculate the Super elevation (e) necessary for 75% design speed[0.75V] and assume no lateral friction is developed
As per practical conditions, it is suggested that superelevation should be provided to fully counteract the centrifugal force due to 75% of the Design Speed(V) by neglecting lateral friction (f=0) developed. Methods of Superelevation
Super Elevation formula = e + f = [V2]/127R
Consider lateral friction f = 0;
75% of design speed which means V= 0.75V
As per formula,
e + f = [V2]/127R
e + 0 = [0.75V]2/127R Methods of Superelevation
e = V2 / 225R
Note: e value should not be more than 0.07
If the calculated value (ecal) is less than (emax) then consider the value of (ecal) if not proceed to next step, Advantages of Superelevation
if (ecal<emax) then e = ecal
If the calculated value (ecal) is greater than (emax) then consider the value of (emax)
if (ecal<emax) then e = emax
Step – 2: How to Calculate Superelevation in Road
Lets assume e = emax = 0.07 and proceed to next step.
Step-3: Calculate the value of friction for ‘e’ Value
Super Elevation formula = e + f = [V2]/127R
= 0.07 +f = [V2]/127R Advantages of Superelevation
f = [V2]/127R – 0.07
Step – 3:
From the above step we found the value of e. Now lets find the value of the lateral friction (f) for the known value of emax Value
Super Elevation = emax + f = [V2]/127R
= 0.07 + f = [V2]/127R
fcal = [V2/127R] – 0.07 Advantages of Superelevation
If fcal < fmax (0.15)
Then fcal = f ;
If fcal > fmax (0.15)
Then e = 0.07 is safe.
But if fcal > 0.15
Then fcal =fmax (0.15)
Step – 4: How to Calculate Superelevation in Road
Lets calculate the value of Restricted Speed (Va)V = [127R(0.22)]1/2
If Va > V then e = 0.07, f = 0.15

Method of Providing Superelevation to the Roads
Superelevation plays an important role to counteract the centrifugal force which is acting on the vehicle moving from the horizontal curve of the road. The attainment of superelevation in roads is done into two parts- Elimination of the Crown and the cambered section
- Rotation of the pavement by attaining full superelevation
Elimination of the Crown and the Cambered Section
Method – 1:
In the first method, the outer half of the cross slope is rotated about the crown at the rate such that the surface of road falls on the same plane and the elevation of the centre line is not varied.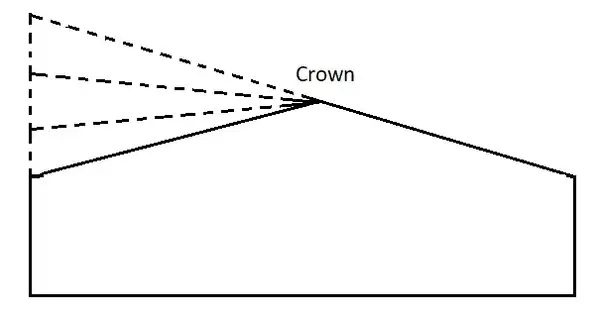
Method – 2:
In the second method, the crown is gradually shifted by increasing the width of the inner half of the cross-section.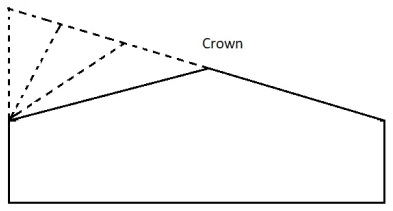
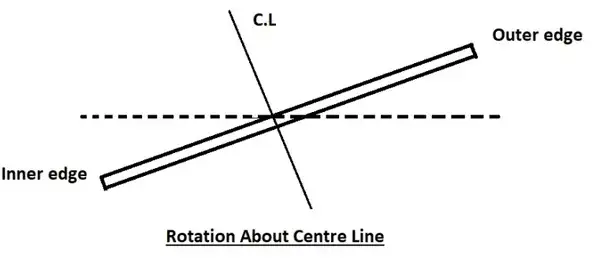
Rotation of the pavement by attaining full Superelevation
In this method, the inner edge of the road is made the pivot point. The Crown, as well as the outer edge, are raised in such a way that the full amount of superelevation is achieved.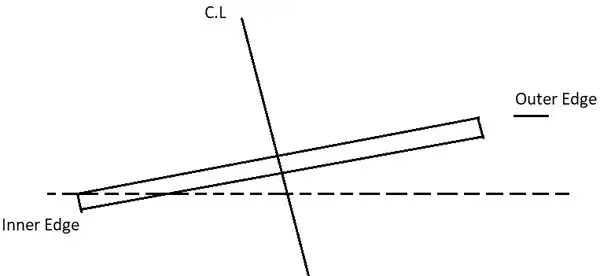
NOTES for How to Calculate Superelevation in Road
Superelevation:
Superelevation is the transverse slope provided to counteract the effect of centrifugal force and reduce the tendency of the vehicle to overturn and to skid laterally outwards by raising the pavement outer edge with respect to the inner edge. Superelevation is represented by “ e ”. Superelevation in Highway Engineering.Super Elevations:
Super elevation is tilting the roadway to help offset centripetal forces developed as the vehicle goes around a curve. Along with friction they are what keeps a vehicle from going off the road. A super elevated section is proceeded by a transition section.Superelevation Formula:
The rate of change in superelevation is found by dividing the difference between normal crown and full super by the transition length. 11000 – 10971.61 = 28.39. The rate of change is the same as for the transition at the beginning end of the curve.OTHER POSTS:
-
Basics of Bar Bending Schedule Formulas | BBS Formulas with Example
-
Bar Bending Schedule for RCC Box Culvert in Excel | Download Sheet
-
Quantity of Cement, Sand & Water required for Plastering Estimate
-
How to Calculate No of Bricks in One Cft, Wall, Room and Building
-
What is Hidden Beam or Concealed Beam | Advantages & Disadvantages
Conclusion:
Full article on What is Superelevation | Superelevation of Road Formula | Maximum Superelevation | Methods of Superelevation | How to Calculate Superelevation in Road | Superelevation Calculation | Advantages of Superelevation | Superelevation in Highways. Thank you for the full reading of this article in “The Civil Engineering” platform in English. If you find this post helpful, then help others by sharing it on social media. If any formula of BBS is missing from this article please tell me in comments.


2 Comments
I would like to see more at of this article
Thanks for the comments please visit more articles by clicking on “All Posts” tab of the Menu Bar